Day-01: AWS Certified Solutions Architect Associate
An end-to-end about AWS Service with LABs
Whats AWS?
AWS (Amazon Web Services) is a Cloud Provider
They Provide you with Servers that you can use on
DemandandscaleeasilyAWS has revolutionized IT over time
AWS Powers some of the biggest websites in the world
Netflix
What we'll learn in this course (and More!)?

we gonna have a walkthrough on all the services which shown in the above screenshot.
AWS Global Infrastructure
AWS Regions
AWS Availability Zones
AWS Data Centers
AWS Edge Locations / Points of Presence
AWS Regions
AWS has Regions all around the world
Names can be us-east-1, eu-west-3....
A region is a cluster of data centers
Most AWS services are region-scoped

How to choose an AWS Region?
if you need to launch an new application , where should you do it?
Compliance: With data governance and legal requirements: data never leaves a region without your explicit permission
Proximity: to customer: reduced latency
Available Services: Within a Region: new services and new features aren't available in every Region.
Pricing: Pricing varies region to region and is transparent in the service pricing page.
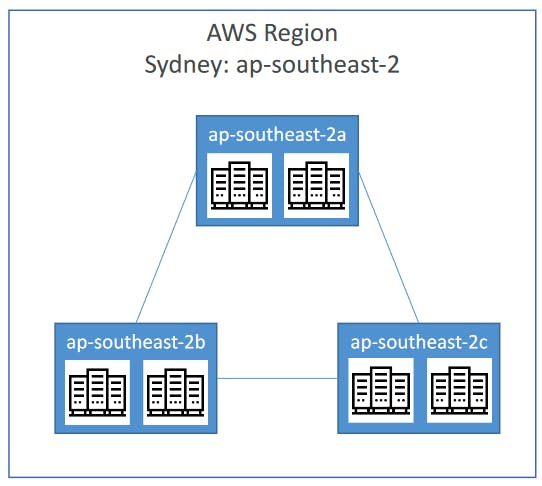
AWS Availability Zones
Each region has many availability Zones ( usually 3, mi s 3 and max is 6) .
Example:
- ap-southeast-2a
- ap-southeast-2b
- ap-southeast-2c
Each availability zone (AZ) is one or more discreet data centers with redundant power, networking and connectivity.
They're separate from each other, so that they're isolated from distaters.
They're connected with high bandwidth, ultra-low latency networking.
AWS Points of Presence (Edge Locations)
Amazon has 400+ points of presence(400+ Edge Locations & 10+ Regional caches) in 90+ cities across 40+ countries.
Content is delivered to end users with lower latency
Tour of the AWS Console
AWS has Global Services:
Identity and Access Management (IAM)
Route53 (DNS service)
Cloudfront (content Delivery Network)
WAF (web application firewall)
Most AWS services are Region-Scoped:
Amazon EC2 (infrastructure as service)
Elastic Beanstalk (platform as a service)
Lambda (Function as a service)
Rekognition (software as a service)
IAM Section
IAM: Users & Groups
IAM = Identity and Access Management, Global service
Root account created by default, shouldn't be used or shared.
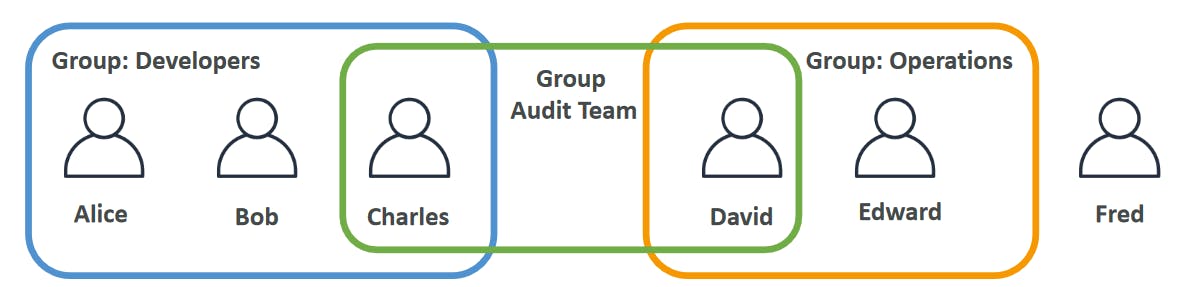
Users are people within your Organisation, and can be grouped
Groups only contain users, not other groups
Users don't have to belong to a group, and user can belong to multiple groups.
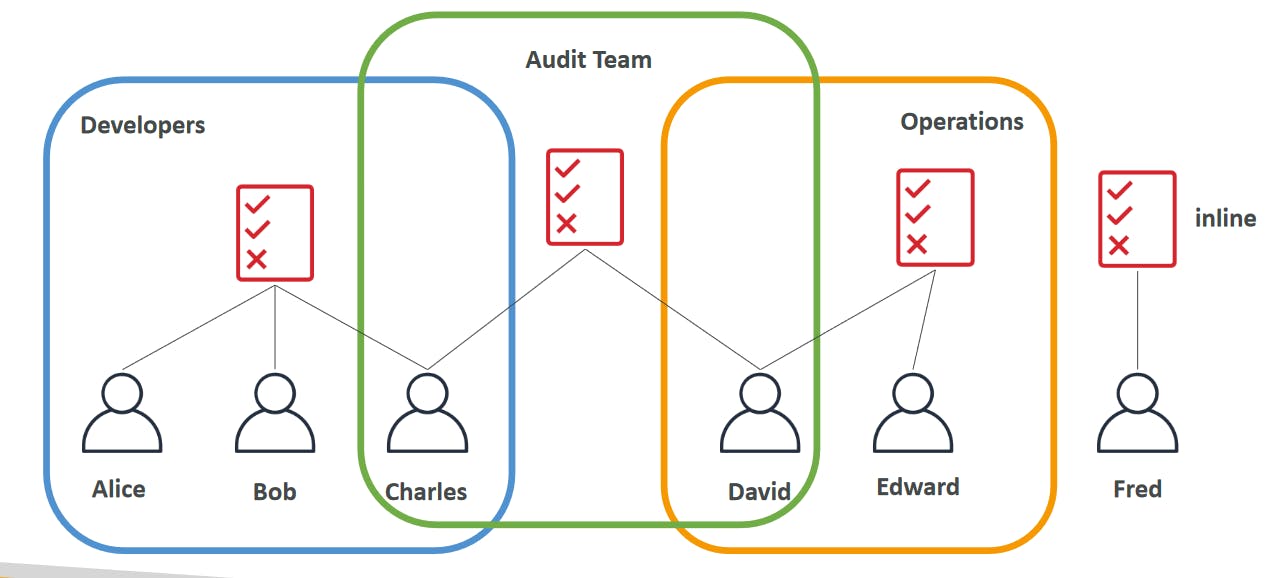
IAM: Permissions
Users or Groups can be assigned JSON documents called policies
These policies define the permissions of the users
In AWS you apply the least privilege principle; don't give more permissions than a user needs.

IAM Policies inheritence
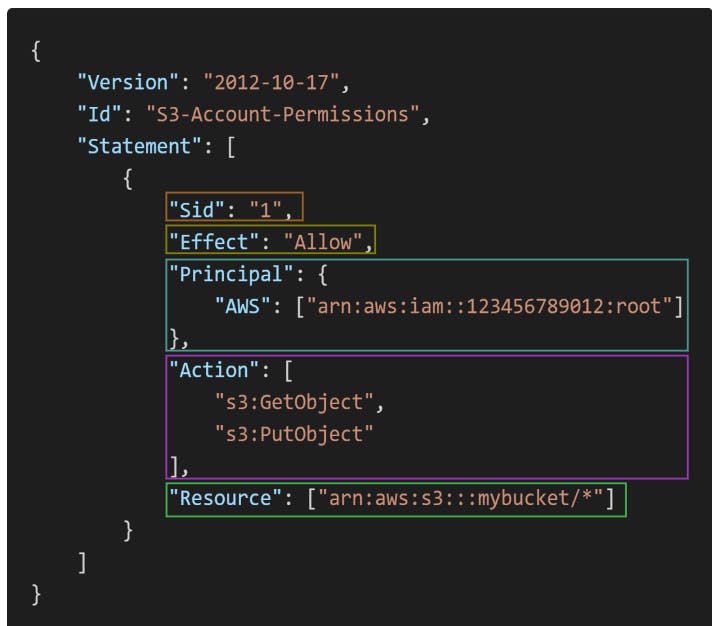
IAM Policies Structure
Consists of
Version: Policy language version, always include 2012-10-17"
ID: an identifier for the policy (optional)
Statement: one or more individual statements (required)
Statements Consists of
Sid: an identifier for the statement (optional)
effect: whether the statement allows or denies access (allow, Deny)
Principal: Account/user/role to which this policy applied to
Action: List of actions this policy allows or denies
Resources: List of resources to which the actions applied to
Condition: Conditions for when this policy is in effect (optional)
IAM - Password Policy
Strong passwords = higher security for your account
In AWS, you can setup a password policy;
set a minimum password length
Required specific character types;
including uppercase letters
lowercase letters
numbers
non-alphanumeric characters
Allow all IAM users to change their own passwords
Require Users to change their passwords after some time (password expiration)
prevent password re-use
Multi Factor Authentication - MFA
Users have access to your account and can possibly change configurations or delete resources in your AWS account.
You want to protect your root Accounts and IAM users
MFA = Password you know + Security device you own

- Main benefits of MFA:
if a password is stolen or hacked, the account is not compromised
How can Users access AWS?
To access AWS, you have three options:
AWS Management Console (protected by password + MFA)
AWS Command Line Interface (CLI): protected by access keys
AWS Software Developer kit (SDK) - for code: protected by access keys
Access keys are generated through the AWS console
Users manage their own access keys
Access keys are secret, just like a password. Dont share them
Access Key ID = Username
Secret Access Key = Password
Example (fake) Access Keys
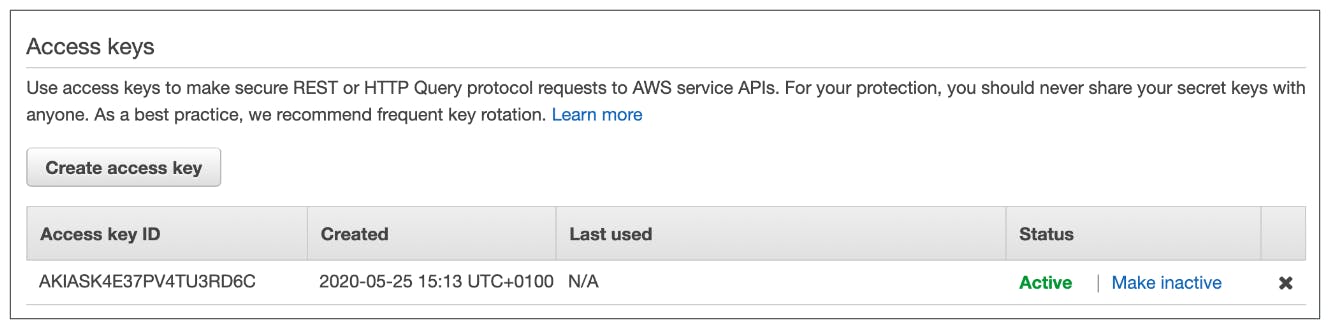
Access key ID: AKIASK4E37PV4983d6C
Secret Access Key: AZPN3zojWozWCndIjhB0Unh8239a1bzbzO5fqqkZq
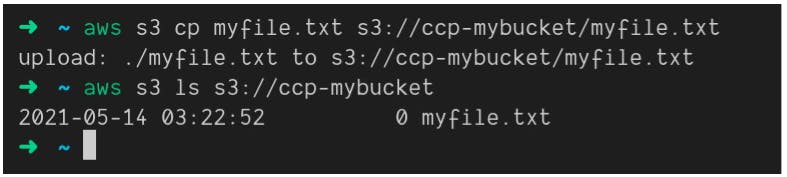
What's the AWS CLI?
A tool that enables you to interact with AWS Services using commands in your command-line shell
Direct access to the public APIs of AWS services.
You can develop scripts to manage your resources.
Its open-source github.com/aws/aws-cli
Alternative to using AWS Management Console
What's the AWS SDK?
AWS Software Development kit (AWS SDK)
Language-specific APIs (set of libraries)
Enables you to access and manage AWS services programmatically.
Embedded within your application
Supports
SDKs (javascript, python, PHP, NET, Ruby, JAVA, Go, Node.js, c++ )
Mobile SDKs (Android, iOS,...)
IoT Device SDKs (Embedded C, Arduino..)
Example: AWS CLI is built on AWS SDK for python
IAM Roles for Services
Some AWS Service will need to perform actions on your behalf
To do so, we will assign permissions to AWS services with IAM Roles
Common roles:
EC2 Instance Roles
Lambda Function Roles
Roles for CloudFormation
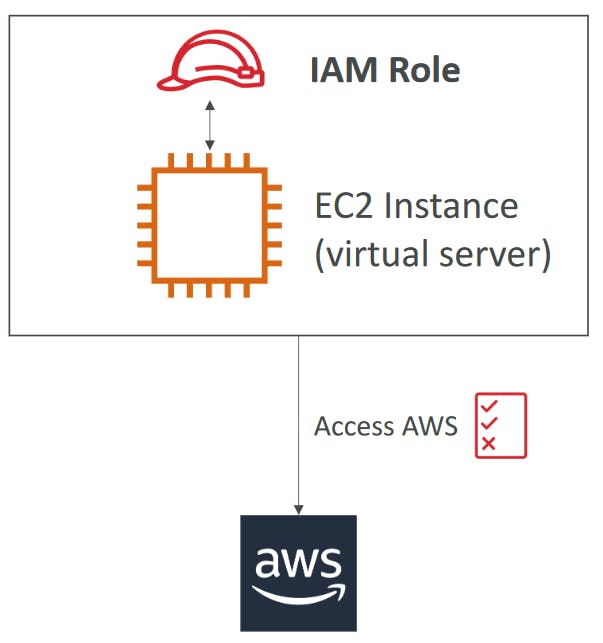
*AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM)* roles are entities you create and assign specific permissions to that allow trusted identities such as workforce identities and applications to perform actions in AWS. When your trusted identities assume IAM roles, they are granted only the permissions scoped by those IAM roles. Using IAM roles is a security best practice because roles provide temporary credentials that do not need to be rotated.
IAM Security Tools
IAM Credentials Report (account-level)
- a report that lists all your account's users and the status of their various credentials
IAM Access Advisor (user-level)
Access Advisor shows the service permissions granted to a user and when those services were last accessed
You can use this information to revise your policies
IAM Guidelines & Best Practices
Don't use the root account except for aws account setup
One physical user = One AWS user
Assign Users to groups and assign permissions to groups
Create a strong password policy
Use and enforce the use of Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Create and Use Roles for giving permissions to AWS services
User Access keys for programmatic Access (CLI/ SDK)
Audit permissions of your account using the IAM Credentials Report & IAM Access Advisor
Never share IAM Users & Access Keys
IAM Section - Summary
Users: Mapped to a physical user, has password for AWS Console
Groups: Contains Users only
Policies: JSON document that outlines permissions for users or groups
Roles: for EC2 instances or AWS services
Security: MFA + Password Policy
AWS CLI: manage your AWS services using the command-line
AWS SDK: manage your AWS services using a programming language
Access Keys: access AWS using the CLI or SDK
Audit: IAM Credentials Reports & IAM Access Advisor
